Time is everything when it comes to breast cancer care. If we can embrace smarter technology, this will help to provide better workflow efficiency and clinical confidence across the patient pathway, unlocking that much needed time to care for breast cancer patients. Tim Simpson General manager, UK and Ireland at Hologic explores how we can achieve this across the breast health continuum of care.
More accurate and efficient detection is instrumental for better patient outcomes. 3D Mammography™ systems have become smarter, bringing breast cancer diagnosis to a new level, improving cancer detection accuracy, optimising workflow, and supporting personalised patient care[1]. The integrated AI powered software solutions employ machine-learning and deep learning algorithms developed and trained on a large number of tomosynthesis (3D Mammography™) images to aid cancer detection, assess breast density, and accelerate diagnosis.
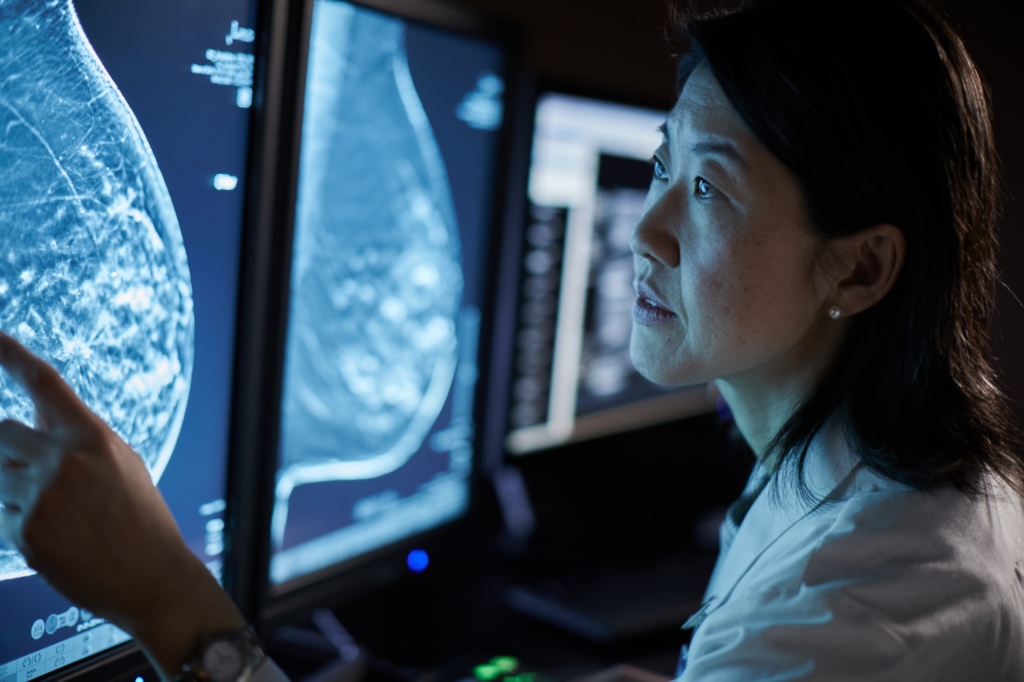
What’s more, using 3D Mammography™ can result in up to 40% fewer recalls[2], [3], helping to reduce the physical and emotional burden on patients and giving back valuable time to health care professionals.
To mitigate the time challenges typically faced when reporting tomosynthesis images, advanced imaging technology can reconstruct high-resolution tomosynthesis slices which results in a reduction in radiologist reading time.
More efficient detection can also be achieved when performing a contrast mammography examination. It’s possible to combine the power of Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM) with 2D and tomosynthesis images all in one compression to provide anatomical and functional imaging in a singular exam. The use of comprehensive imaging using co-registered functional and morphological information can reduce reading time to seven – ten minutes versus thirty to sixty minutes for a standard breast MRI[4],[5].
Almost 43% of women over 40 years old have dense breast tissue that can obscure lesions on traditional 2D mammograms, making cancers harder to detect and recalls more likely[6]. Women with very dense breasts have a four to five times greater risk of developing breast cancer in comparison to women with less dense breasts[7].
This is where new AI–powered technologies have the potential to help identify women who are particularly at high risk of breast cancer, specifically those women with extremely dense breasts.
Assessing women using automated breast density analysis software is a simple way to ensure that those most at risk of developing breast cancer are prioritised for screening, on potentially a more regular basis, whilst the screening interval for those women at lower risk could be extended, creating a more efficient and personalised breast screening program in the longer term.
Diagnostic innovation is on a trajectory that we cannot ignore. It is evident that AI is sure to revolutionise healthcare. There will be multiple benefits associated with the adoption of AI technology in breast imaging for patients and clinicians alike; for example, enhanced clinical confidence, improved workflow efficiencies, accelerated disease detection and increased accuracy of breast cancer diagnosis. Hologic is proud to be leading the way with its AI solutions for our customers and partners, helping to save time and lives across the breast health continuum of care.
1 Philpotts L, Kalra V, Crenshaw J, Butler R ‐ Radiological Society of North America 2013, SSK01‐09
[2] Friedewald SM, Rafferty EA, Rose SL, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. JAMA. 2014 Jun 25;311(24):2499-507.
[3] Olivia DiPrete, Ana P. Lourenco , Grayson L. Baird, Martha B. Nov 2017. Mainiero. Screening Digital Mammography Recall Rate: Does It Change with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Experience?. Radiology: Volume 286: Number 3—March 2018
[4] Cancer.org. 2022. What Is a Breast MRI? | Breast Cancer Screening. [online] Available at: <https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/screening-tests-and-early-detection/breast-mri-scans.html> [Accessed 28 April 2022].
[5] Julie Sogani,a Victoria L. Mango,a Delia Keating,a Janice S. Sung,a and Maxine S. Jochelson. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: Past, Present, and Future. Clin Imaging. 2021 Jan; 69: 269–279.
[6] Sprague BL, Gangnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106(10), 2014.
[7] Ingrid Schreer. Dense Breast Tissue as an Important Risk Factor for Breast Cancer and Implications for Early Detection. Breast Care (Basel). 2009 May; 4(2): 89–92.
ADS-03644-EUR-EN Rev 002
See the latest BIR special publication on Breast Imaging and AI


